Reducing the environmental burden
One of the most significant problems of traffic in towns and villages is air pollution with emissions that bear risks for human health. Traffic produces a vast amount of pollutants and burdens the inhabitants with excessive noise.
Therefore, we offer you a complex solution to the problem:
- We conduct systematic research, monitor and assess the environmental burden caused by traffic, including potential health risks.
- We determine and assess select indicators of environmental burdens, including their trends.
- We design methodological instructions or expert studies, including the propositions leading to the reducing of the environmental burden caused by traffic, for you.
Choose from our range of services:
Measuring the quality of air as specified by Act No. 201/2012 Coll., Air Protection Act
We measure the concentrations of the following pollutants in the atmosphere, as listed in Act No. 201/2012 Coll., authorized by the Ministry of the Environment: nitrogen dioxide, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, tropospheric ozone, benzene, solid particles PM10 and PM2.5, arsen, cadmium, nickel, lead and benzo[a]pyrene.
Measuring other pollutants may be added:
- Sulfane, nitrous oxide, nitrogen oxides, carbon dioxide, volatile organic compounds (general)
The measuring is conducted using the Airpointer® (Recordum Messtechnik GmbH, Austria) device. It may be undertaken at two locations simultaneously. The length of the measuring depends on the requirements of the submitter, various designs of measuring may be agreed upon. - Aromatic hydrocarbons (toluene, ethylbenzene, o-xylene, m,p-xylenes) and 1.3-butadiene
The measuring is conducted using the VOC71M (ENVIRONMENT SA, France) device. We can measure continuously in 15-minute intervals. - Measuring the size distribution of solid particles of fractions PM1.0, PM2.5 and PM10, measuring the numerical concentrations of particles in 32 size fractions from 250 nm to 32 µm
The measuring is conducted using the EnvironCheck 107 (Grimm aerosol technik, Germany) device. - Measuring the size distribution of solid particles with aerodynamic diameters from 6 nm to 10 µm, i.e. including nanoparticles, numerical concentrations of particles in 14 size fractions from 6 nm to 10 µm, i.e. including nanoparticles
The measuring is conducted using the ELPI® + (Dekati Ltd., Finland) device. - Taking samples of solid particles of fractions PM1.0, PM2.5 and PM10
The measuring is conducted using the Leckel MVS6 (Sven Leckel Ingenierbüro GmbH, Germany) and TSP using the PS-1 (Graseby-Andersen, USA) devices. - Taking samples of solid particles with aerodynamic diameters from 15 nm to 10 µm in 13 size intervals, i.e. including nanoparticles
The measuring is conducted using the ELPI® + (Dekati Ltd., Finland) device. - Monitoring the morphology of solid particles, including the elementary constitution of individual particles
We use the scanning electrone microscope (SEM) VEGA TS 5136 LSU (Tescan s.r.o., Czechia) with the energy dispersive analyser (EDX) Quantax XFlash® 6 (Bruker Nano GmbH, Germany). - Determining the concentrations of elements in samples of solid particles, including heavy and platinum metals
The measuring is conducted using the 8800 ICP-QQQ-MS (Agilent Technologies, Japan) device. - Determining the concentrations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) in samples of solid particles
The measuring is conducted using the QP 2010 GC/MS (Shimadzu, Japan) and GC MS/MS Triple Quadrupole 7000C a GC 7890B (Agilent Technologies, Japan) devices. - Determining the concentrations of volatile aromatic hydrocarbons (BTEX) in the atmosphere using thermal desorption
We use the GC MS/MS Triple Quadrupole 7000C, GC 7890B and Mini Thermal Desorber7667A (Agilent Technologies, Japan) system.
The measuring may be conducted at two locations simultanesously, the length as required, other designs of measuring may be agreed upon as well.
Air quality measurements in city parks
We can use air quality measuring principles in other locations, for example in city parks. Air quality information may help you to plan, develop and maintain these important green spaces in cities.
We provide a full service that includes:
- placing measuring devices,
- sampling on filters,
- analysing the samples in our accredited laboratory and
- visualizing the results into concentration rosettes in the map.
You can find more information in this product datasheet.
If you want to know the air quality in your park or another location, contact us for a non-binding offer to measure pollutants.
Informative price: 1 800 – 6 500 Kč/day based on the extent of the requested measuring and the distance from Brno
Reference: Hlavní město Praha, 2013-2014
Hydrotrajekt, Banská Bystrica, Slovensko, 2014-2015
Assessment of environmental contamination
We offer complex evaluation of environmental contamination at a specifical location, as well as individual elements of the environment. We use our own laboratories, equipped with top instruments, for taking environmental samples and their processing and preparation for chemical and toxicological analyses. Our lab then provides the resulting qualitative and quantitative determination from a wide range of organic and inorganic substances, including their trace and ultra-trace concentrations.
Evaluation of air contamination:
IInformation may be found in the chapter Measuring the quality of air as specified by Act No. 201/2012 Coll., Air Protection Act.
Assessment of soil contamination:
- Homogenisation of samples, preparation of water leaches using the analytical sieving machine AS 300 Control, jaw crusher BB 50, sample divider PT 100 and oscillating mill MM 400 (all Retsch, Germany),
- eSample extraction and decomposition using the microwave device Speed Wave four (Berghoff GmbH, Germany),
- Determining the concentrations of elements, including heavy and platinum metals, using the 8800 ICP-QQQ-MS (Agilent Technologies, Japan) device,
- Extraction of soil samples using the extraction system for solid-liquid extractions based on the „fluidized bed extraction“ principle (IKA RET control – VISC, (IKA, Germany) extractor,
- Determining the concentrations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) using the QP 2010 GC/MS (Shimadzu, Japan) and GC MS/MS Triple Quadrupole 7000C a GC 7890B (Agilent Technologies, Japan) devices,
- Determining the cation exchange capacity – by titration, pH – laboratory pH/conductometer Orion (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., USA),
- Toxicity tests of water leaches of soil samples:
Inhibition of freshwater green algae growth test,
Inhibition of mobility of the crustacean Daphnia magna test,
Inhibition of the germination of Sinapis alba test – all in accordance with standardized procedures using these devices: spectrophotometer INFINITE M 200 Pro Nanoquant (Tecan Group Ltd., Switzerland), laboratory pH/conductometer Orion (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., USA), digital lux meter Testo 545 (TESTO, Czechia), thermostated chamber TS 606/2-Var (WTW instruments, GmbH, Germany) and other equipment.
Assessment of building materials, secondary materials and waste:
- Homogenisation of samples, preparation of water leaches using the analytical sieving machine AS 300 Control, jaw crusher BB 50, sample divider PT 100 and oscillating mill MM 400 (all Retsch, Germany),
- Sample decomposition using the microwave device Speed Wave four (Berghoff GmbH, Germany),
- Determining the concentrations of elements, including heavy and platinum metals, using the 8800 ICP-QQQ-MS (Agilent Technologies, Japan) device,
- Extraction of soil samples using the extraction system for solid-liquid extractions based on the „fluidized bed extraction“ principle (IKA RET control – VISC, (IKA, Germany) extractor,
- Determining the concentrations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) using the QP 2010 GC/MS (Shimadzu, Japan) and GC MS/MS Triple Quadrupole 7000C a GC 7890B (Agilent Technologies, Japan) devices,
- Toxicity tests of water leaches of material and waste samples:
Inhibition of freshwater green algae growth test,
Inhibition of the germination of Sinapis alba test – all in accordance with standardized procedures using these devices: spectrophotometer INFINITE M 200 Pro Nanoquant (Tecan Group Ltd., Switzerland), laboratory pH/conductometer Orion (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., USA), digital lux meter Testo 545 (TESTO, Czechia), thermostated chamber TS 606/2-Var (WTW instruments, GmbH, Germany) and other equipment
Assessment of water contamination:
- Measuring the pH levels and conductivity on-site (when sampling – pH) using the conductometer Ysi Professional Plus (Ysi Inc., USA).
- Determining the concentrations of elements, including heavy and platinum metals, using the 8800 ICP-QQQ-MS (Agilent Technologies, Japan) device,
- Determining the concentrations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) using the QP 2010 GC/MS (Shimadzu, Japan) device and the GC MS/MS Triple Quadrupole 7000C a GC 7890B (Agilent Technologies, Japan) systems,
- Toxicity tests of water samples:
Inhibition of freshwater green algae growth test,
Inhibition of mobility of the crustacean Daphnia magna test,
Inhibition of the germination of Sinapis alba test – all in accordance with standardized procedures using these devices: spectrophotometer INFINITE M 200 Pro Nanoquant (Tecan Group Ltd., Switzerland), laboratory pH/conductometer Orion (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., USA), digital lux meter Testo 545 (TESTO, Czechia), thermostated chamber TS 606/2-Var (WTW instruments, GmbH, Germany) and other equipment
Measuring the emissions of vehicles in real traffic
Measuring the emissions of vehicles in real traffic contains: the continuous measuring of concentrations of gaseous emissions of O2, CO, CO2, HC and NOx, isokinetic sampling of solid particles, isokinetic sampling of gases, including unlimited pollutants, placed into containers for previously non-specified detailed laboratory analysis of gas emissions, sampling for two different driving regimes, measuring the flow of exhaust gases, measuring the pressure and temperature of exhaust gases. Everything is done using a devicce developed by the Transport Research Centre and the company SEKO spol. s r.o.
The device has the following advantages: pairing the signals from the measuring instruments with a GPS signal, quick and easy mounting to the examined vehicle (equipped with a towing device), the chance to transfer the instrument placed on a palette on/in the examined vehicle (not equipped with a towing device – trucks, train engines etc.), the chance to use independent modules for the measuring of gaseous emissions (for cars not equipped with a pulling device), measuring on a cylindrical dynamometer, useable on a closed testing track and in real traffic, measuring road vehicles as well as off-road vehicles and machines.
Data processing contains:
- The calculation of emissions and fuel consumption from a complete data sample,
- The calculation of emissions and fuel consumption following the PEMS procedure (selective, comparable to the homological cycle, helps to determine the conformity factor – tolerance for the life-span of the vehicle).
Driving cycles:
- Defined beforehand (standardized, specific),
- Traffic:
- Standard route – comparable measuring
- Following the PEMS procedure - a random route with a given ratio of urban, extramural and motorway traffic.
The issues of fuels and lubricants
The offer contains:
- Specification of the interpretation of emission measuring results,
- Substantiation of the anomalies in emission characteristics of vehicles,
- Influence on the emission factors of vehicles,
- Specification of inputs for emissions modelling (AP development scenario),
- The impact of alternative fuels on the degradation of motor oil,
- Analysis of the technical condition of vehicles based on motor oil.
Using the device Nicolet iS5 - Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., USA.
Traffic-caused emissions balance calculations
Our services involve balancing emissions of mobile sources from road traffic (including emissions of solid pollutants from abrasions and VOC emissions from evaporation from the fuel systems of petrol vehicles), railway, air and water traffic, as well as emissions from off-road sources (agricultural, forrest and construction vehicles, military vehicles, plant care etc.).
The calculation of traffic-caused emissions is conducted with our own methodology. The model calculation that is used makes use of data from traffic statistics, data about the sale of fuels, the structure of the fleet and estimates of the annual mileage of the individual vehicle categories. The emissions are determined using the calculated rate of fuel consumption of the individual vehicle categories and the respective emission factors. In accordance with the methodology for determining the emissions within the emission ceiling directive, only emissions of domestic and international traffic during the take-off and landing phase (the so-called LTO cycle) are taken into account for air traffic, and the emissions during the flight phase, as well as those of planes just flying over, are not included in the balance.
Noise modelling
We conduct noise modelling for the purpose of strategic noise mapping and creation of action plans (in accordance with 2002/49/ES). Additionally, we provide background data for spatial planning, general plans of transport and the designing of anti-noise measures. Noise models are also offered to investors to help assess and plan new projects and objects.
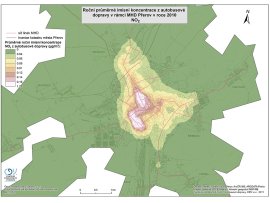
Modelling traffic emissions and the contribution of traffic to imission concentrations
The offer involves modelling the flow of emissions from traffic at a specific location and the creation of dispersion studies (modelling the contribution of traffic to the imission concentrations). The input for these modellings is a multi-modal traffic figure. If the client does not have a traffic model available, its creation may be a part of the offer.
The specific price depends on the size of the location, quantity and difficulty of transport-organizational analyses, the number of scenarios and the number of evaluated pollutants. An essential impact on the price may also be the need to create the traffic model and its detail.
Modelling the traffic imission concentrations (dispersion study)
We conduct the calculation of imission concentrations for both gaseous and solid pollutants from traffic in accordance with the SYMOS'97 directive. Primarily, when substances are evaluated, the limits of which are given by the Air Protection Act No. 201/2012 Coll. When required, other pollutants may be modelled, as well.
The dispersion study analyses:
- The maximum short-term imission concentrations,
- The average annual concentrations,
- The intervals of hourly imission concentrations,
- The consideration of background pollution,
- The evaluation for particularly sensitive locations, such as the surroundings of schools, sports fields, residential areas, etc.,
- The comparison of model concentrations with imission limits,
- The time of exeeding the limit values,
- The comparison with the station measurements provided by the ČHMÚ.
The price depends on the size of the modelled area, from which the length of data preparation and calculation time derive.
Measuring accoustic pressure in the protected outdoor area of a building
We conduct the measuring in accordance with Standard ISO 1996-1 and 1996-2 in accredited mode – verification of compliance with noise limits in the protected outdoor area of buildings. Should this contain traffic noise, the price includes a vehicle census.
Consultations with issues of noise load and preventing excessive traffic noise
The offer contains consultations, designs of potential solutions, precaution propositions, etc.
Processing accoustic studies
Noise maps, action plans, simulations of troubled areas, simulations of anti-noise measures, calculations of population affected by excessive noise and monetary explication of externalities stemming from noise load, etc.The offer includes:
- The processing of noise maps,
- Action plans,
- Simulations of troubled areas,
- Simulations of anti-noise measures,
- Calculations of population affected by excessive noise and monetary explication of externalities stemming from noise load.
Measuring road surface noisiness over its entire length using the CPX method
The offer includes accredited measuring of the noisiness of any road surface using the CPX (Close-ProXimity) method, the verification of the effectivity of low-noise surfaces, a comparison of the noisiness of individual types of surfaces in various points of their life span..
Analyses for the implementation of alternative fuels and propulsions in a fleet
We conduct the economic and non-economic (technical, organisational, etc.) analyses for the managerial decisions about the implementation of vehicles operating with alternative fuels and vehicles with alternative propulsions into a fleet.
The price depends on the quantity and difficulty of cunducted analyses.
Optimalisation of alternative fuel infrastructure placement in a given area
We offer to design a draft for the optimal placement of alternative fuel filling stations and recharging infrastructure in a defined area.
Systems supporting clean vehicles in cities
We design concepts supporting clean vehicles, using the tools in the competence of territorial self-governing units, which may be used to improve the environment in cities and higher territorial units.
The actual price depends on the size of the area, the quantity and difficulty of conducted analyses (traffic-organisational, economic, technological), the quantity of evaluated precautions and influences on the quality of the atmosphere (the number of scenarios and pollutants). An essential impact on the price may also be the need to create a traffic model..
Issues of countryside fragmentation by transport infrastructure
The consultations include, above all, the assessment of potential passability of transport infrastructure for wild living animals, the identification of critical places, propositions for possible precautions to improve the passability, etc.
The price depends on the extent of the handled communications and other requirements in the individual task.
ROAD KILL (SRAŽENÁ ZVĚŘ) – web-based app serves to better understand the deaths of animals on roads and railways
Every day, tens or hundreds of animals are killed on roads and railways in the Czech Republic. Our app brings a nation-wide summary of the species of road kill and places where the collisions happen most frequently. This way, we help to better understand the circumstances under which these accidents occur.
The data is used by departments responsible for hunting on various levels of self-government, hunting guild managers, county hunting guilds, and also those interested in traffic safety and nature protetion.
Should you have information about animals killed in collisions with motor vehicles, please add them to the database. All you have to do is register.
A detailed map of collisions with wildlife available here.
Contact:
Photogallery